For the first time we have install it in our system.
- sudo apt-get install unrar
After install, go to the folder which contain the .rar file
Type unrar command :
unrar e filename.rar
Done
support indonesia go open source program

aMSN is a free open source MSN Messenger clone, with features such as:
Adopted from http://tombuntu.com
This guest article was written by Vivek Kumar from TNerd.com, a blog focused on technology news, tricks and tips and Linux tutorials.
Linux has come a long way in support for multimedia and graphics. Today we will see how to transform Ubuntu 8.10 into a media center platform. You can achieve this using various software like MythTV and Boxee, but we’re going to use XBMC Media Center (formerly XBox Media Center).
Before going into the process of installing and configuring XBMC let’s take a look at what it offers.

Home Page: http://xbmc.org/
Description: XBMC is an award winning media center application for Linux, Mac OS X, Windows and XBox. The ultimate hub for all your media, XBMC is easy to use, looks slick, and has a large helpful community.
Features of XBMC
A complete list of features can be found here.
Installation
Open System->Administration->Software Sources and select the Third Party Software tab. Add the following software source:deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/team-xbmc-intrepid/ubuntu intrepid main
Close Software Sources and when prompted, choose to reload the repositories.
Install XBMC from the package xbmc (click the link to install), or by running the command below in your terminal:sudo apt-get install xbmc
Optionally you can also install:
sudo apt-get install xbmc-skin-*sudo apt-get install xbmc-eventclients-*sudo apt-get install xbmc-scripts-example Starting and Running XBMC
All that is left now is to start XBMC. You can start XMBC by going to Applications->Sounds & Video->XBMC Media Center.
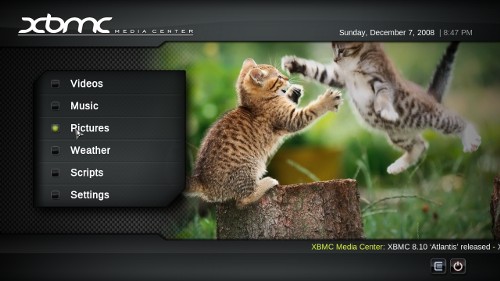
Here are two tips to get you started:
The interface is pretty user friendly, so feel free to explore.

Ubuntu and other Debian-based distributions utilize a special tool for managing packages known as APT. APT is able to automagically install all of the needed dependencies for a software package, as well as keep the package up to date, by scanning what are known as APT repositories. Debian-based distributions have their own repositories of software that include Wine, however we keep our own repository of the latest available beta packages here for download.
The packages here are beta packages. This means they will periodically suffer from regressions, and as a result an update may break functionality in Wine. If the latest stable release of Wine (currently Wine 1.0.1) works for you, then you may not want to use these beta packages.
Open the Software Sources menu by going to System->Administration->Software Sources. Then select the Third Party Software tab and click Add.
 Administration->Software Sources->Third Party Software" border="0" height="509" width="531">
Administration->Software Sources->Third Party Software" border="0" height="509" width="531"> Then, copy and paste one of the lines below depending on which version you are running.
For Ubuntu Intrepid (8.10):
deb http://wine.budgetdedicated.com/apt intrepid main #WineHQ - Ubuntu 8.10 "Intrepid Ibex"
For Ubuntu Hardy (8.04):
deb http://wine.budgetdedicated.com/apt hardy main #WineHQ - Ubuntu 8.04 "Hardy Heron"
For Debian Etch (4.0):
deb http://wine.budgetdedicated.com/apt etch main #WineHQ - Debian 4.0 "Etch"
After adding the repository, you also need to add the key for the repository to your system's list of trusted keys.
Download and save Scott Ritchie's key to your desktop. Then open the Authentication tab, click import key file, and select the key file you just saved (Scott Ritchie.gpg). It is safe to delete this file after doing this step.
 Administration->Software Sources->Authentication" border="0" height="509" width="531">
Administration->Software Sources->Authentication" border="0" height="509" width="531"> Click close to finish, and then reload the package information. If you have Wine installed, the system's update manager will now inform you of the latest Wine beta release and prompt you to upgrade. If you haven't installed Wine yet, go to Applications->Add/Remove and search for Wine.
An alternate method for adding the Wine repositories and installing Wine is through the command line, as follows:
First, open a terminal window (Applications->Accessories->Terminal). On Debian, you will need to open a root terminal. Then add the repository's key to your system's list of trusted APT keys by copy and pasting the following into your terminal:
wget -q http://wine.budgetdedicated.com/apt/387EE263.gpg -O- | sudo apt-key add -
Next, add the repository to your system's list of APT sources:
For Ubuntu Intrepid (8.10):
sudo wget http://wine.budgetdedicated.com/apt/sources.list.d/intrepid.list -O /etc/apt/sources.list.d/winehq.list
For Ubuntu Hardy (8.04):
sudo wget http://wine.budgetdedicated.com/apt/sources.list.d/hardy.list -O /etc/apt/sources.list.d/winehq.list
For Debian Etch (4.0):
sudo wget http://wine.budgetdedicated.com/apt/sources.list.d/etch.list -O /etc/apt/sources.list.d/winehq.list
Then update APT's package information by running 'sudo apt-get update'.
If you are using Ubuntu, you can now install Wine by clicking this link. Alternatively, you can install by going to Applications->Add/Remove and searching for Wine.
If you are upgrading the entire system, such as going from Ubuntu 8.04 to 8.10, you will need to come back to this page and add the repository for the new version above. The built in update manager will not switch the Wine repository automatically.
Since the APT repository can only hold the latest packages, older versions of the packages are available at the WineHQ .deb packages archive.
You can install downloaded packages by double-clicking on them.